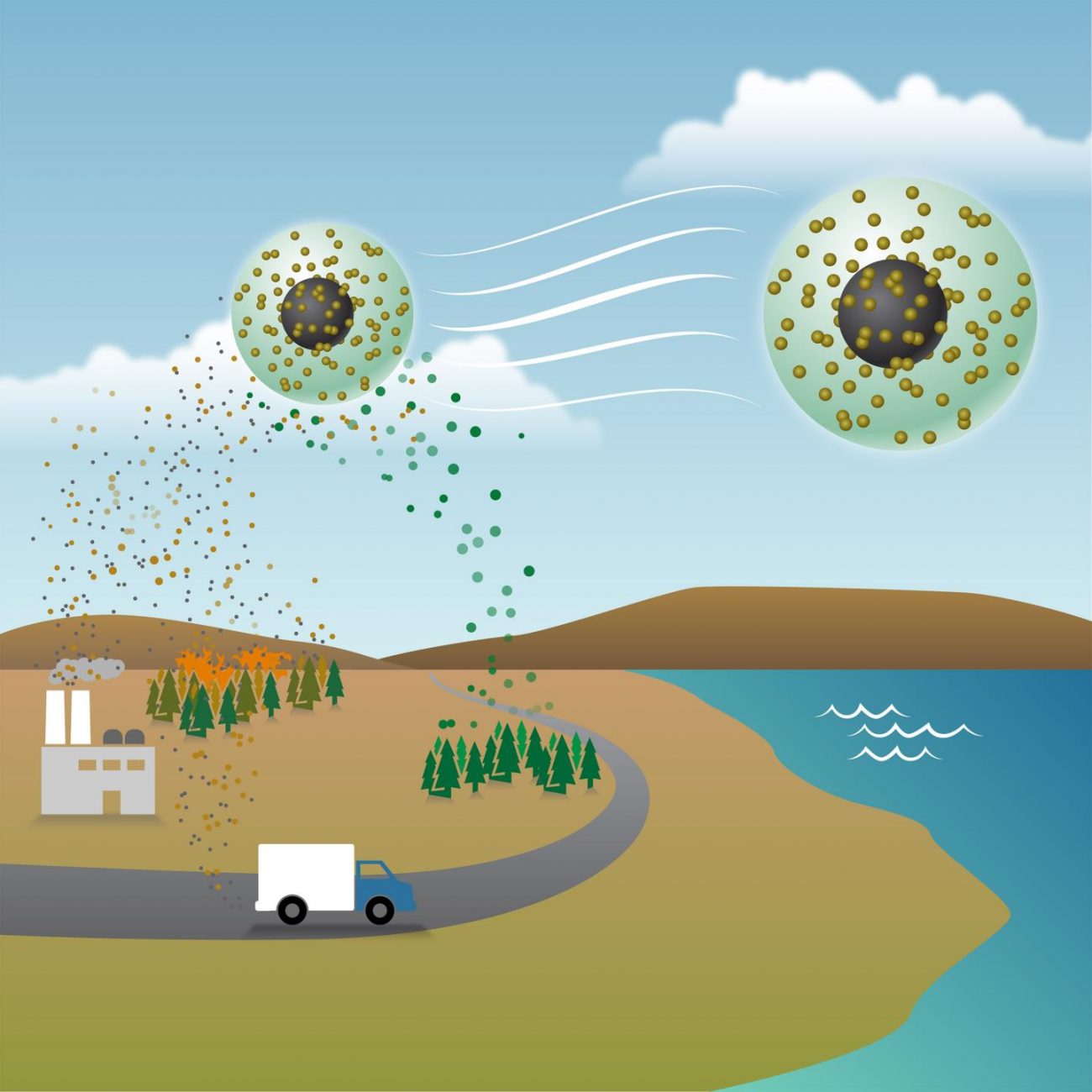
CORVALLIS, Ore. — A new way of looking at how pollutants ride through the atmosphere has quadrupled the estimate of global lung cancer risk from a pollutant caused by combustion, to a level that is now double the allowable limit recommended by the World Health Organization. The findings, published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences …
Tag Archive
Below you'll find a list of all posts that have been tagged as “Anhui”